Mammography is the process of using low energy X-ray (usually around 30 KVP) to examine the human breast, which is used as diagnostic and screening tool. A mammography exam is also called as mammogram. The goal of mammography is the early detection of breast cancer typically through detection of characteristic masses and / or micro-calcifications.
Digital mammography:
It is also known as full field digital mammography (FFDM). The replacement of x-ray film by solid state detectors converts x-ray into electrical signals. It is quite same as the detectors found in the digital cameras. These electrical signals are used to produce images of the breast to be seen on a digital platform like a monitor or special film similar to conventional mammograms. As a general frame of references having a digital mammogram is essential same as conventional film mammogram.
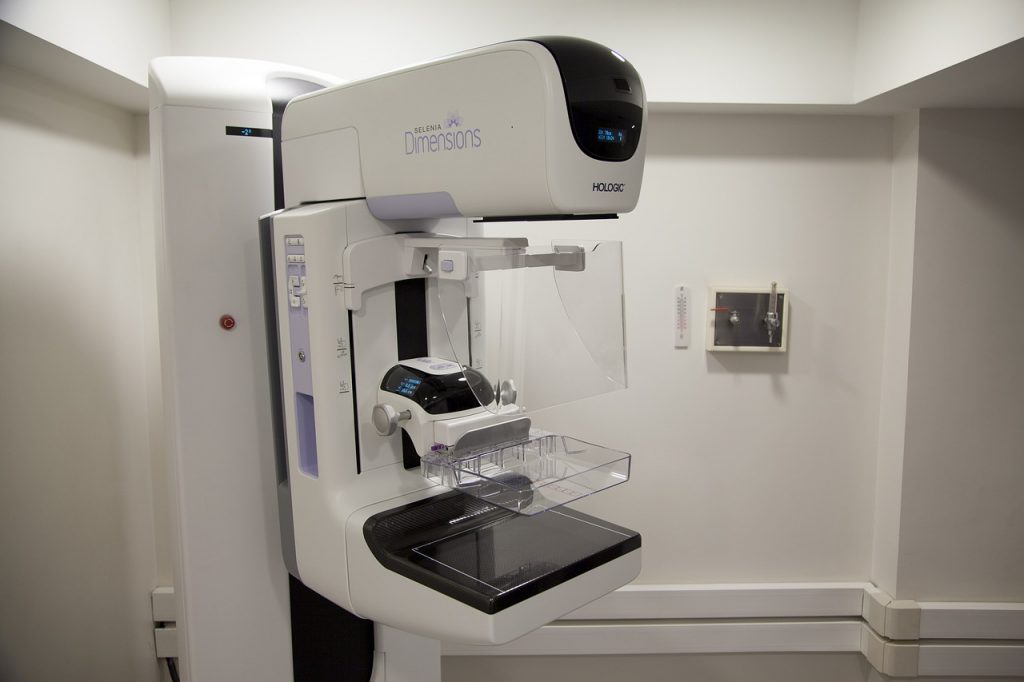
Screening Mammography:
Even before a patient line missing or the symptoms of cancer. Mammography can detect breast cancer. The guidelines from U.S. department of health and human services (HHS), the American cancer society (ACS), the American cancer society (ACS), the American medical association (AMA) and the American college of Radiology (ACR) suggests mammography every year for every women stepping at age of 40. At early stages breast cancers is curable. Research has shown that annual mammograms can save many lives.
In addition to this the National Cancer institute (NCI) has recommended that women have had breast cancer and those who are at risk due to genetic history of breast cancer should seek medical advice for frequent diagnosis and diagnosis before age of 40.
Diagnostic Mammography:
Abnormal clinical findings like breast lump or lumps found by the person or by her doctor can be evaluated by diagnostic mammography.

